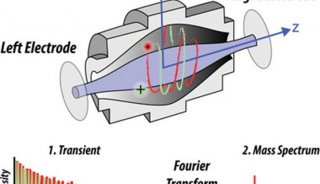
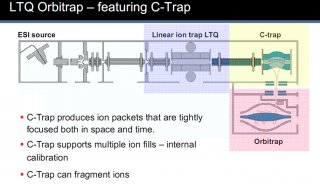
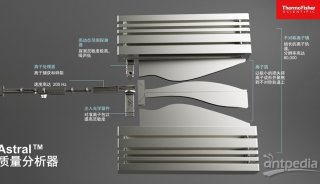
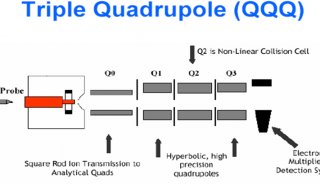
2010全國質譜大會大會報告(四)
中國科學院大連化學物理研究所 許國旺研究員
來自中國科學院大連化學物理研究所的許國旺研究員做了題為“液相色譜-質譜用于代謝標志物的發現和鑒定”的報告。許老師提出,現在是一個組學的時代,代謝組學作為最主要的組學之一,目前在疾病研究、藥物研發及職務和微生物等領域均得到重視。
代謝組學是研究小分子(相對分子質量小于1, 000)一個十分有用的工具,它以組織、體液或細胞為研究對象。一般來說,代謝組學的研究包括樣品采集、預處理、代謝組數據采集、多變量數據分析、標志物發現和識別及最終的生物解釋幾方面。由于缺乏數據庫樣本及標樣,代謝標志物的識別是研究的一個瓶頸。
許老師在報告中,講述了基于色譜-質譜聯用技術的集成識別策略,包括多變量數據分析、精確分子量測定、質譜碎片裂解規律、色譜保留規律、餾分微制備、親和色譜、酶解等。并列舉了藥物作用機理和疾病標志物的代謝組學研究作為實例闡述了這一集成策略。
Wisconsin-Madison(威斯康星-麥迪遜)大學 Li,Lingjun(李靈軍)教授
來自Wisconsin-Madison(威斯康星-麥迪遜)大學的Li,Lingjun(李靈軍)教授,做了題為“Probing Neuronal Communication via Novel Mass Spectral Strategies”(用新型質譜技術探索神經通訊)的報告。她首先介紹了神經肽在細胞間通訊中至關重要的作用,這些聚合多肽在化學信使調節,和在神經電路中測定它們的功能中具有重要作用。甲殼動物具有較簡單和已被充分研究的神經系統,可作為很好的模型系統來發展分析方法,并觀測神經肽豐富的全部細節是如何來精細調節神經電路,并在細胞和神經網絡水平產生多種輸出。使用高靈敏度的基于質譜的多肽圖和從頭測序方法,發現了大量的新型多肽,并發現即使一個相對簡單的神經元網絡,同樣包含了未被預期的豐富多樣的神經肽。另外,質譜成像技術和活體微透析取樣工具,可史無前例地對神經肽分布和分泌的細節進行追蹤。對于完成對生物活性的神經肽的功能發現的目標,發展了建立在同位素甲醛標記和多同位素標記(N,N-二甲基亮氨酸)的新型定量技術基礎上的方法,可對不同生理條件下的神經肽組進行區分顯示。李教授介紹了神經肽在攝食行為和環境壓力下的調節。總而言之,這種多肽組學結合生理學的研究,有助于闡釋在調節神經網絡可塑性方面,神經肽扮演的功能。以下是英文摘要:
Neuropeptides make up the largest and the most complex signaling molecules used in intercellular communication. Because of critical roles that these polypeptides play in the regulation of chemical messengers and determine their functions in the neural circuitry. The simpler and well-characterized crustacean nervous system provides an excellent model system to facilitate analytical method development and to investigate how a rich repertoire of neuropeptides can fine tune a well-defined neural circuit that produces multiple outputs at the cellular and network levels. Using a highly sensitive mass spectrometry-based peptide profiling and de novo sequencing strategy, a large number of novel peptides have been discovered, revealing that even a relatively simple neural network contains an unexpectedly-rich diversity of neuropeptides. Furthermore, both mass spectrometric imaging techniques and in vivo microdialysis sampling tools have been implemented to follow neuropeptide distribution and secretion in unprecedented details. Towards the goal of functional discovery of bioactive neuropeptides, novel quantitative schemes based on isotopic formaldehyde labeling and multiplexed isobaric labeling based on N.N-dimethylated leucine have been developed to produce differential display of neuropeptidomes under different physiological. Example of neuropeptide regulation of feeding behavior and environmental stress will be described in this presentation. Collectively, these combined peptidomic and physiological studies will help to elucidate the function roles that neuropeptides play in regulating neural network plasticity.
加拿大Alberta大學 Le,Chris(樂曉春)教授
來自加拿大Alberta大學的Le,Chris(樂曉春)教授,做了題為“Mass Spectromety and Affinty Chromatography Techniques for Studying Arsenic-binding Proteins in Human Cells”(在研究人類細胞中砷結合蛋白中的質譜和親和色譜技術)的報告。砷中毒對于疾病、環境等的影響眾所周知,但砷中毒的機理還不清楚,可能是三價砷結合了蛋白的硫基團,因此改變了蛋白的構象抑制了蛋白功能。為研究與蛋白作用的砷,課題組開發了一種親和選擇技術并與串聯質譜聯用,從大量的細胞蛋白中選擇和鑒定特定的與砷結合的蛋白。受控實驗使用包含游離半胱氨酸或非活性半胱氨酸的蛋白,顯示砷親和柱特異捕獲游離的半胱氨酸。該方法被應用到牛膽綠素還原酶B、A549人肺癌細胞亞細胞器組分等研究中。使用親和色譜-串聯質譜方法鑒定大量的砷結合蛋白,因為其重要的生物功能引起科學家的關注。實驗證實砷可以結合細胞提取物的蛋白質,而砷如何影響生物系統中的蛋白功能,需要繼續研究活體細胞中砷和蛋白的相互作用才能確認。以下是英文摘要:
Arsenic is one of the most important environmental agents in causing chronic human disease. Elevated levels of arsenic drinking water may affect >100 million people around the world .A wide variety of adverse health effects, most seriously, cancers of bladder, lung, urinary tract, and skin, have been attributed to chronic exposure to arsenic . However, the biochemical mechanisms responsible for these effects caused by arsenic remain unclear ,but may be mediated by the binding of trivalent arsenicals to thiol groups in proteins, thereby changing the conformation of these proteins and inhibiting their functions. If some of the affected proteins are responsible for cellular repair of DNA damage, for example, the inhibition of these proteins could lead to carcinogenesis.
To study interaction of arsenic with proteins, we have developed an affinity selection technique, coupled with mass spectrometry, to select and identify specific arsenic-binding proteins from a large pool of cellular proteins. Controlled experiments using proteins either containing free cysteine(s) or inactive cysteine showed that the arsenic affinity column specifically captured the proteins containing free cysteine(s) available to bind tu arsenic .The technique was able to capture and identify trace amounts of bovine biliverdin reductase B present as a minor impurty in the commercial preparation of carbonic anhydrase II ,demonstrate the ability to identify arsenic-binding proteins in the presence of a large excess of non-specific proteins. application of the technique to the analysis of subcellular fractions of A549 human lung carcinoma cells identified 50 proteins in the analysis of subcellular fraction ,and 24 proteins in the membrane/ organelle fraction that could bind to arsenic .This added substantially to the current list of only a few known arsenic-binding proteins.
A mumber of arsenic-binding proteins identified using the affinity chromatography tandem mass spectrometry approach were of particular interest because of their important biological functions .For example ,DNA-dependent protein kinase, ATP-dependent helicase II (Ku 70),and topoismerase 2 alpha , are involved in DNA repair and maintaining genome stability .several other proteins modulate the redox status of cells , e.g . peroxiredoxin-1 and thioredoxin ,and apoptosis ,e.g.,lamin A and heat shock cognate protein .this work shows that arsenic can bind to these proteins in cells extracts。How arsenic affects the function of these proteins in biological systems will have to be confirmed by studying arsenic interaction with proteins in living cells.