企業簡介
旭月(北京)科技有限公司(http://xuyue.net),是2005年創立于中關村科技園區的國家高新技術企業。創始人許越先生,曾服務于美國航空航天局NASA,是現代“非損傷微測技術(NMT)”奠基人,動態分離子組學(imOmics)創始人,NMT產業化倡導者,美國揚格公司(http://youngerusa.com)現任總裁。
聯系方式
電話:010-82622628
公司地址:北京市海淀區蘇州街49-3號盈智大廈601
郵 編:100080......
Plant Biotechnology Journal丨NMT驗證兩種基因型甜高粱鎘積累的差異
上一篇 /
下一篇 2019-06-10 10:58:20/ 個人分類:公司新聞
期刊:Plant Biotechnology Journal
標題:Comparative
transcriptome combined with morphophysiological analyses revealed key
factors for differential cadmium accumulation in two contrasting sweet
sorghum genotypes
通訊作者:中科院植物研究所李銀心,已用NMT發表3篇SCI文獻
英文摘要
Cadmium
(Cd) is a widespread soil contaminant threatening human health. As an
ideal energy plant, sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) has
great potential in phytoremediation of Cd-polluted soils, although the
molecular mechanisms are largely unknown.
In
this study, key factors responsible for differential Cd accumulation
between two contrasting sweet sorghum genotypes (high-Cd accumulation
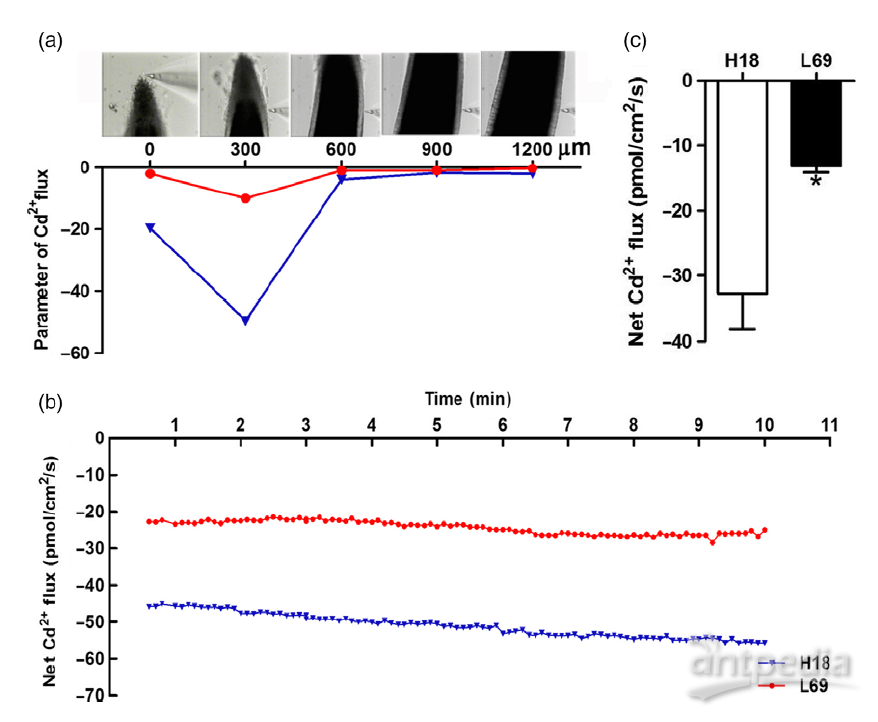
one H18, and low-Cd accumulation one L69) were investigated. H18
exhibited a much higher ability of Cd uptake and translocation than L69.
Furthermore, Cd uptake through symplasmic pathway and Cd concentrations
in xylem sap were both higher in H18 than those in L69. Root anatomy
observation found the endodermal apoplasmic barriers were much stronger
in L69, which may restrict the Cd loading into xylem.
The
molecular mechanisms underlying these morpho-physiological traits were
further dissected by comparative transcriptome analysis. Many genes
involved in cell wall modification and heavy metal transport were found
to be Cd responsive DEGs and/or DEGs between these two genotypes. KEGG
pathway analysis found phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway was
overrepresented, indicating this pathway may play important roles in
differential Cd accumulation between two genotypes.
Based
on these results, a schematic representation of main processes involved
in differential Cd uptake and translocation in H18 and L69 is proposed,
which suggests that higher Cd accumulation in H18 depends on a
multilevel coordination of efficient Cd uptake and transport, including
efficient root uptake and xylem loading, less root cell wall binding,
and weaker endodermal apoplasmic barriers.
中文摘要(谷歌機翻譯)
鎘(Cd)是一種廣泛的土壤污染物,威脅著人類健康。作為一種理想的能源植物,甜高粱(Sorghum bicolor(L.)Moench)在植物修復Cd污染土壤方面具有巨大潛力,盡管其分子機制尚不清楚。
在這項研究中,研究了兩個對比甜高粱基因型(高Cd積累一個H18和低Cd積累一個L69)之間差異Cd積累的關鍵因素。
H18表現出比L69高得多的Cd攝取和易位能力。此外,H18中通過相互作用途徑的Cd攝取和木質部汁液中的Cd濃度均高于L69。根解剖觀察發現L69內胚層質外屏障強度較大,可能將Cd負荷限制在木質部。
通過比較轉錄組分析進一步解剖這些形態生理學性狀的分子機制。發現參與細胞壁修飾和重金屬轉運的許多基因是這兩種基因型之間的Cd響應性DEG和/或DEG。 KEGG途徑分析發現苯丙烷類生物合成途徑過多,表明該途徑可能在兩種基因型之間的差異性Cd積累中起重要作用。
基于這些結果,提出了H18和L69中差異性Cd吸收和轉運的主要過程的示意圖,這表明H18中較高的Cd積累依賴于有效Cd吸收和轉運的多級協調,包括有效的根吸收和木質部負荷,較少的根細胞壁結合,和較弱的內胚層質外障礙。
文章鏈接:
https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12795
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.002
旭月版權所有,轉載注明出處.


配圖
導入論壇收藏
分享給好友
推薦到圈子
管理
舉報
TAG: